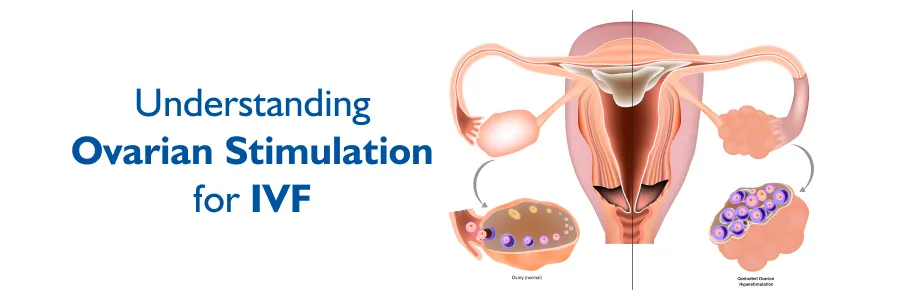
Normally, a woman after attaining menarche will produce one egg per month around 14th day after menstrual period. For In Vitro fertilisation & embryo Culture program, one egg may not suffice and the whole procedure and success depend on the number and quality of the eggs obtained. So, we hyper stimulate the ovaries in a safe manner using a method called controlled ovarian hyperstimulation by “Down Regulation” under long protocol or short protocol (Agonist / Antagonist). After downregulating the system, we give Hormone injections of International Quality e.g., Recombinant FSH, Recombinant LH, highly purified FSH, HMG, etc which helps the wife to produce more number of better quality eggs. The dose depends on the age, weight and the Basal hormonal status of the women.
Why is Ovarian Stimulation Necessary?
- In natural cycles, only one egg is usually released per month, limiting the chances of fertilization.
- Ovarian stimulation enhances the number of viable eggs, improving IVF and IUI outcomes.
- It helps in retrieving multiple eggs, allowing for embryo selection and freezing options for future cycles.
The Ovarian Stimulation Process
1. Initial Assessment & Baseline Testing
Before starting the stimulation process, our fertility specialists conduct a thorough evaluation, including:
- Hormonal blood tests (FSH, LH, AMH, and Estradiol)
- Transvaginal ultrasound to assess ovarian reserve and antral follicle count
- Medical history review and personalized treatment planning
2. Administration of Ovarian Stimulation Medications
Patients receive fertility medications to stimulate the ovaries. These include:
- Gonadotropins (FSH, LH): Injected to promote follicular growth
- Clomiphene Citrate or Letrozole: Sometimes used for mild stimulation
- GnRH Agonists or Antagonists: Used to prevent premature ovulation
3. Monitoring & Follicular Tracking
- Regular ultrasounds and blood tests track follicle development and hormone levels.
- Medications may be adjusted to ensure optimal egg maturation while preventing ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
4. Final Maturation Trigger
- Once follicles reach the desired size, a trigger injection (hCG or GnRH agonist) is administered to induce final egg maturation.
5. Egg Retrieval or Insemination
- In IVF cycles, eggs are retrieved 34-36 hours after the trigger shot.
- In IUI cycles, the trigger shot times ovulation for precise sperm insemination.






